Topic: Data Structures
- arrays and the Sieve of Eratosthenes
February 18,
2016
Arrays store multiple variables of the same type in a row with a single name and an index number.
In most programming languages, the index number is appended inside square brackets: [ ].
Either a number or a variable can be inside square brackets.
By using a variable inside the brackets, a programmer can modified the whole array inside a WHILE loop very easily.
Most programmers use variables named "i" or "index" for the index, but any name can be used.

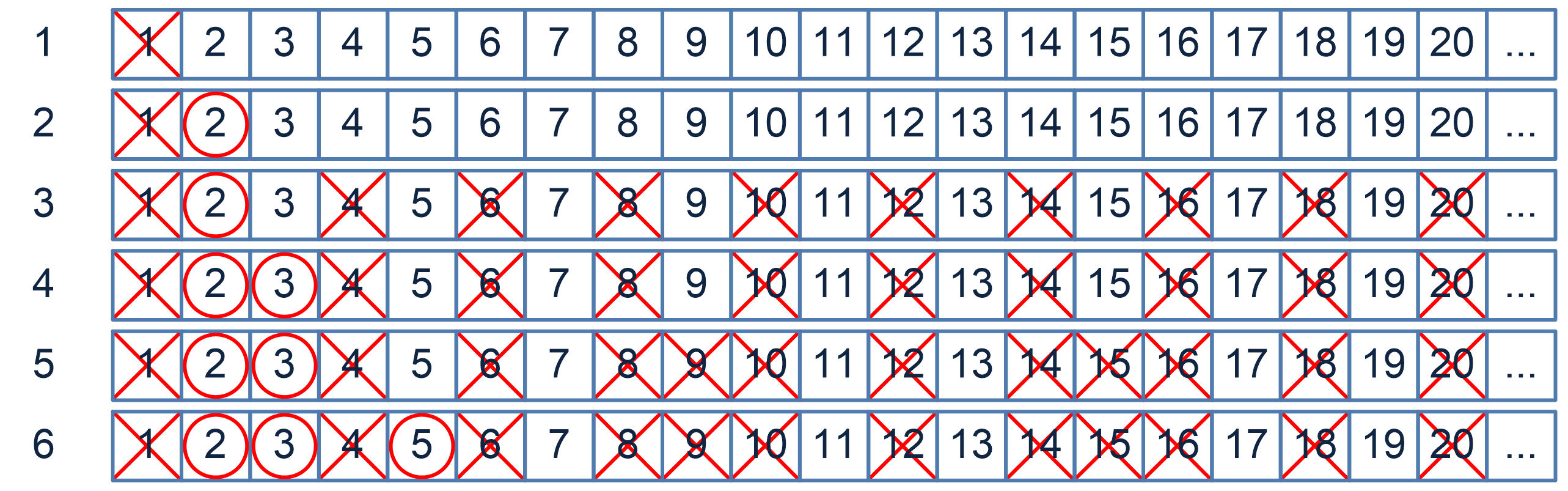
Wikipedia's article on The Sieve of Eratosthenes
Implementation of the Sieve of Eratosthenes in Java
Module Sieve
Const LIMIT AS Boolean = 1000000
Sub Main()
Dim sticks(LIMIT) as Boolean
Call InitializeSticks(sticks);
Call KickDownSticks(sticks);
Call PrintPrimes(sticks)
End Sub
Sub InitializeSticks(ByRef sticks() As Boolean
Dim index As Integer
' All arrays in Visual Basic start at index 0.
' Initialize first two sticks (0 and 1) to false, meaning not prime.
sticks(0) = False
sticks(1) = False
' Initialize the rest of the array as true, meaning a potential prime
index = 2
While (index <= LIMIT)
sticks(index) = True
index = index + 1
End While
End Sub
Sub KickDownSticks(ByRef sticks() As Boolean)
Dim index As Integer
Dim foot As Integer
' Check every stick from 2 to LIMIT
index = 2
While (index <- LIMIT)
' If this stick is true, meaning it is a prime
If (sticks(index) = True) Then
'Kick over every multiple of this stick
foot = index + index
While (foot <= LIMIT)
sticks(foot) = False
foot = foot + index
End While
End IF
' Check next number
index = index + 1
End While
End Sub
Sub PrintPrimes(ByRef sticks() As Boolean)
Dim index As Integer
' Check every stick. If a stick is true
' then it is a prime number. Print it.
index = 0
While (index <= LIMIT)
If (sticks(index) = True)
System.Console.Out.WriteLine(index)
End IF
index = index + 1
End While
End Sub
End Module